🔋
Understanding Capacitors and Their Functions
May 17, 2025
Capacitors and Capacitance: Study Notes for IIT JEE
What is a Capacitor?
- A capacitor (also known as an electric condenser) is a two-terminal electrical component designed to store energy in the form of an electric charge.
- Capacitance varies from small to high storage.

Capacitance in Physics
- Capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy as an electric charge, measured in farads.
- Example: A capacitor storing 9 coulombs with a 9V battery has a capacitance of 1 farad.
Construction of a Capacitor
- Consists of two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric or between metallic plates.
- Conductors can be electrolytes, thin films, or sintered beads of metal.
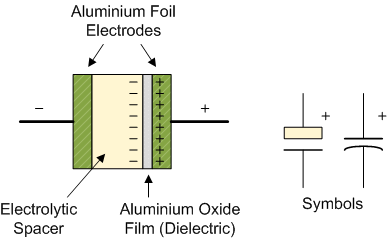
Role of Non-Conducting Dielectric in Capacitors
- Dielectrics increase the capacitor's ability to charge.
- Common dielectrics: Mica, plastic film, glass, paper, ceramic.
Addition of Capacitors
- Capacitors can be added:
- In Series: Total capacitance is less than any single capacitor.
- In Parallel: Total capacitance is the sum of all capacitors.

Capacitor Rating
- Different capacitors can have the same capacitance but different voltage ratings.
- Voltage ratings are important to avoid damage due to excessive voltage.
- Common DC voltage ratings: 10V - 1000V.
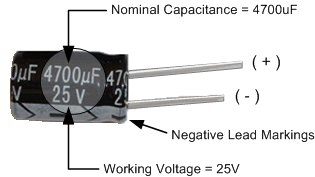
Properties or Characteristics of Capacitors
- Nominal Capacitance (C) - Measured in pF, nF, or micro-Farads.
- Working Voltage (WV) - The maximum applied voltage without failure.
- Tolerance (%) - Variability in capacitance value.
- Leakage Current - Small DC current flow, leading to gradual discharge.
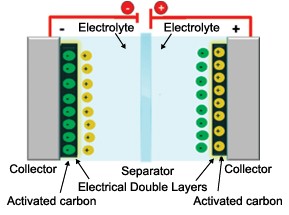
Super Capacitors
- Also known as Electric Double-Layer Capacitors (EDLC), Supercaps, Ultracapacitors, or Goldcaps.
- Higher capacitance but lower voltage limits.
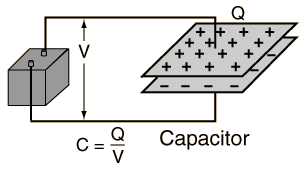
Parallel Plate Capacitor
- Consists of two parallel conductive plates with a dielectric between them.
- Capacitance depends on the dielectric material.

Effect of Dielectric on Capacitance
- Dielectric increases capacitance.
- A dielectric constant (K) measures this effect.
Energy Stored in a Capacitor
- Work done moving charge against repulsion is stored as energy.
- Formula involves capacitance and voltage.
Numerical Examples
- Series Connection: Calculate total capacitance using provided formulas.
- Parallel Connection: Add capacitances directly.
- Capacitors with Given Area and Voltage: Use area and separation to find capacitance.
- Energy Storage Changes: Analyze changes when altering plate distances or connections.