💧
Understanding Hydrogen Bonds in Water
Jun 2, 2025
Hydrogen Bonds in Water
Introduction to Water's Properties
- Human body is 60-70% water.
- Key to life due to unique chemical properties.
- Cellular metabolism occurs in cytosol.
- Water supports life across cells, organisms, and ecosystems.
Polarity of Water Molecules
- Water molecule: two hydrogen atoms bonded to an oxygen atom.
- Bent molecular structure due to unshared electron pairs on oxygen.
- Electrons in water molecule organize in a tetrahedron.
- Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, creating partial charges.
- Water is a polar molecule due to:
- Polar covalent bonds
- Bent shape
Hydrogen Bonding in Water Molecules
- Water molecules attract each other due to polarity.
- Hydrogen bonds form between partial positive hydrogens and electronegative atoms (e.g., oxygen).
- Hydrogen atoms must be attached to electronegative atoms for bonding.
Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Substances
- Hydrophilic: Substances with charge/polarity that dissolve in water.
- Hydrophobic: Nonpolar substances (e.g., oils, fats) do not dissolve in water and remain separate.
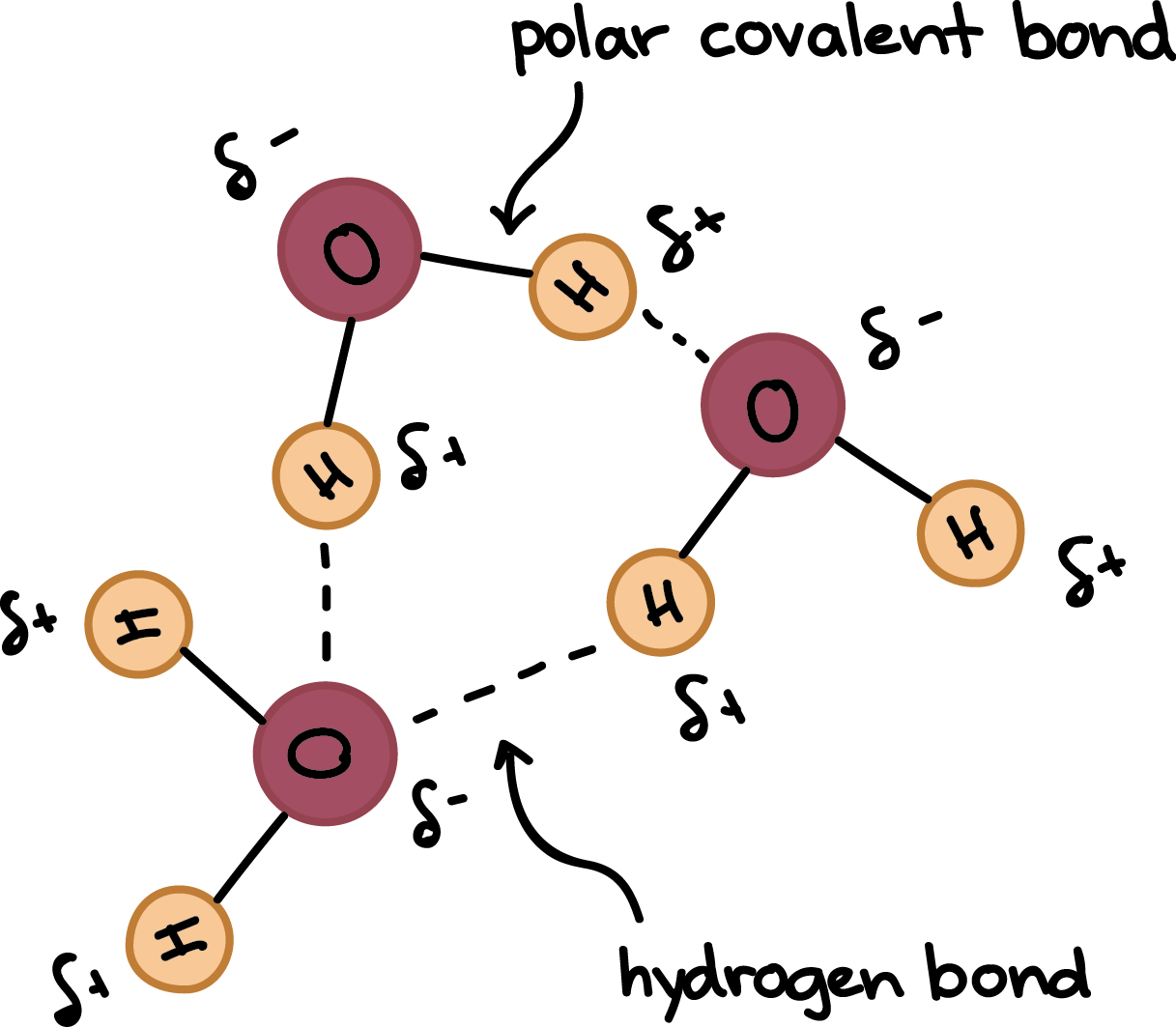
Attribution and References
- Content derived from OpenStax College, Biology, and licensed under CC BY 3.0 and CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
- Further information can be found in Wikipedia articles on water properties and hydrogen bonds, and in textbooks like "Campbell Biology."