🌊
Understanding River Processes in Geography
May 21, 2025
River Processes - Geography IGCSE Revision Notes
Overview
This document provides summary notes for IGCSE Geography on the topic of river processes. It covers key concepts such as erosion, transportation, deposition, and river characteristics. The notes are written by Bridgette Barrett and reviewed by Jenna Quinn.
Erosion
-
Definition: Erosion involves the wearing down of the river channel.
-
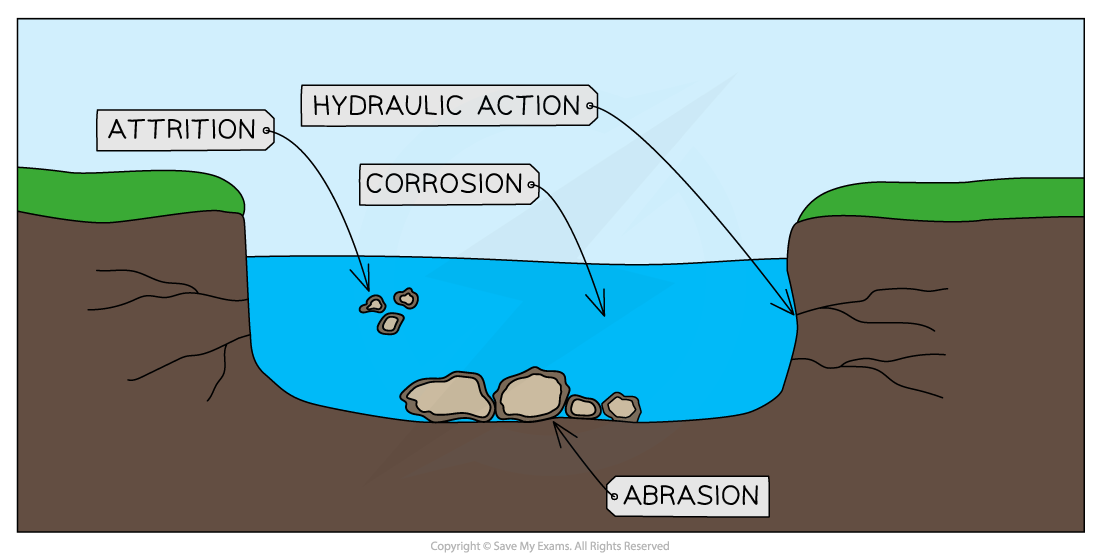
Processes of Erosion:
- Hydraulic Action: The force of water removes material from the river bed and banks.
- Abrasion: Material carried by the river scrapes away the bed and banks.
- Attrition: Material carried by the river collides and becomes smaller and rounder.
- Corrosion (Solution): Rocks dissolve in slightly acidic water.
-
Types of Erosion:
- Vertical Erosion: Predominant in the upper course, deepens the river valley.
- Lateral Erosion: Predominant in the middle and lower courses, widens the river valley.
Transportation
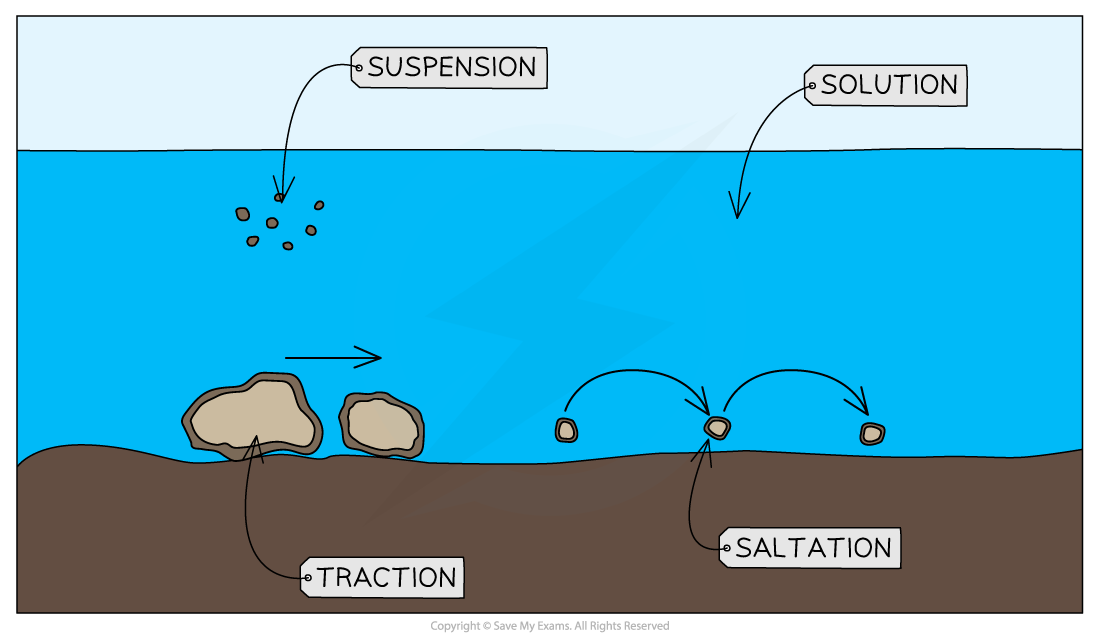
- Processes of Transportation:
- Traction: Larger materials rolled along the riverbed.
- Saltation: Smaller materials bounce along the riverbed.
- Suspension: Light materials carried within the water flow.
- Solution: Materials dissolved in water.
Deposition
- Occurs when a river loses energy and drops its load.
- Causes:
- Reduced discharge due to less precipitation or upstream abstraction.
- Decreased gradient.
- Slowing flow in bends or shallow areas.
- When entering larger bodies of water (sea, ocean, lake).
- Material Deposition:
- Bedload: Heaviest materials dropped first.
- Alluvium: Lighter materials like gravel, sand, silt carried further.
River Characteristics
-
Profiles:
- Long Profile: Shows changes in gradient from source to mouth.
- Typically concave with steep upper course and flatter lower course.
- Cross Profile: Cross-section of the river channel showing depth and width changes.
- Long Profile: Shows changes in gradient from source to mouth.
-
Course Characteristics:
- Upper Course: Shallow, steep sides, narrow, low velocity, large bedload, vertical erosion.
- Middle Course: Wider, deeper, gentle valley sides, higher velocity, lateral erosion.
- Lower Course: Deep, flat, wide, high velocity, deposition dominant.
Examiner Tips
- Differentiate between valley shape and river shape.
- Understand how each process impacts the river channel.
Worked Example
- Provided example analyzes a photograph to explain erosion processes using hydraulic action, abrasion, corrosion, and attrition.
Conclusion
- Rivers are dynamic systems where erosion, transportation, and deposition play key roles in shaping the landscape.
- The river's characteristics change significantly from the source to the mouth due to these processes.