🌒
Understanding Lunar and Solar Eclipses
May 3, 2025
Lecture Notes: Lunar Eclipses and Solar Eclipses
What is an Eclipse?
- An eclipse occurs when a planet or moon obstructs the Sun's light.
- On Earth, we experience two types of eclipses:
- Solar Eclipses
- Lunar Eclipses
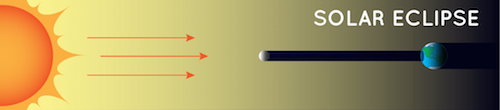
Solar Eclipse
- Definition: Happens when the Moon blocks the Sun's light and casts its shadow on Earth.
- Occurrence:
- Total eclipse occurs roughly every 1.5 years somewhere on Earth.
- Partial eclipses happen at least twice a year.
- Visibility:
- Not everyone can see every solar eclipse.
- Rare to witness a total solar eclipse due to the small shadow cast by the Moon.
- The same location on Earth sees a solar eclipse approximately every 375 years.
- Eye Safety:
- Viewing requires specialized eye protection except during the total phase when the Sun is completely covered by the Moon.
- For more info, visit the NASA Eclipse Safety Page.
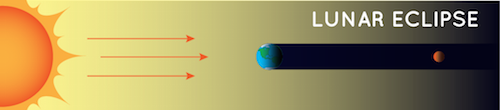
Lunar Eclipse
- Definition: Occurs when Earth blocks the Sun's light from reaching the Moon.
- Appearance:
- The Moon appears reddish during a total lunar eclipse due to Earth's atmosphere bending sunlight (Rayleigh scattering).
- The phenomenon is similar to why sunsets are orange and red.
- Frequency:
- Unlike solar eclipses, lunar eclipses can be seen by many people.
- Occurs when the night side of Earth is facing the Moon during the eclipse.
Why No Monthly Lunar Eclipse?
- The Moon's orbit is tilted compared to Earth's orbit around the Sun.
- This tilt means the Moon often misses Earth's shadow.
Remembering the Difference
- Solar Eclipse: The Sun gets darker.
- Lunar Eclipse: The Moon gets darker.
Additional Resources for Educators
Note: Illustrations in the resource are not to scale. Credit for all diagrams: NASA/JPL-Caltech.